
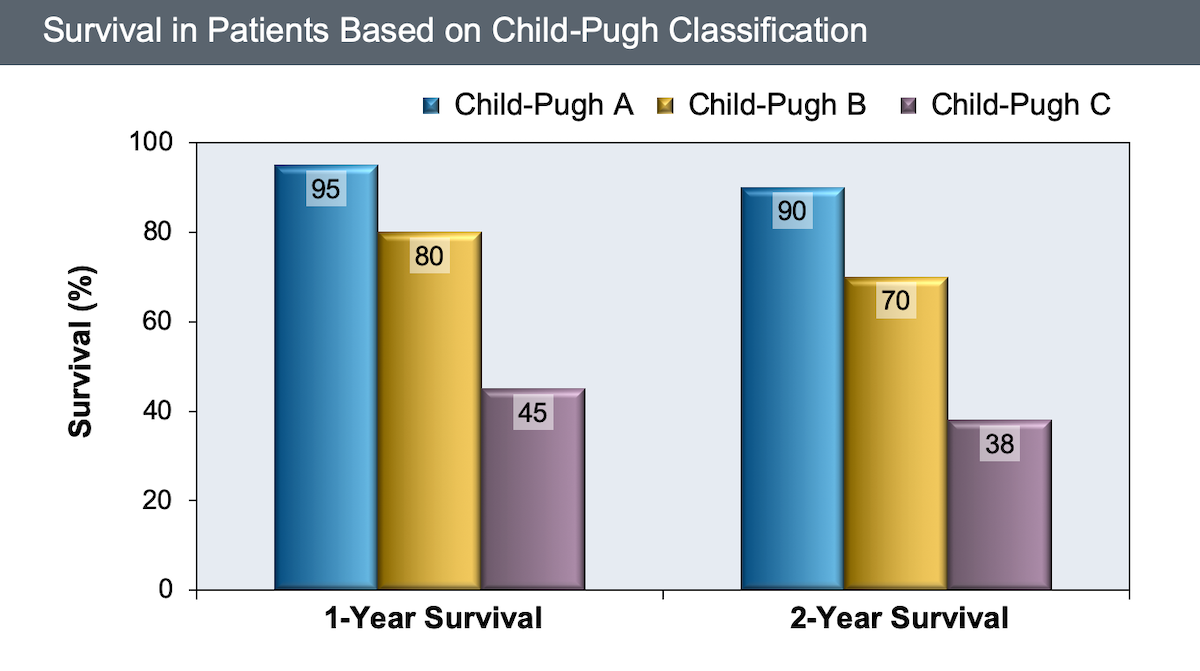
It has been shown that a high SOFA score for any given organ is associated with significantly higher mortality. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score has been developed and is basically used to assess and classify the variable degrees of organ dysfunction. The Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II, a physiologically based prognostic system, is a widely used severity of illness scale used to predict hospital mortality in all ICU patients. One of the most commonly used scores is the Child-Turcotte-Pugh score (CTP), a widely used system used to risk stratify cirrhotic patients. This necessitated the development of a number of prognostic scoring systems to estimate the clinical outcome of HE in clinical practice. HE is associated with a poor survival outcome and a high risk of in-hospital mortality. HE is either associated with acute liver failure (type A), portosystemic bypass with no intrinsic hepatocellular disease (type B) or liver cirrhosis, and portal hypertension and/or portosystemic shunts (type C). In addition, vasodilatation, caused principally by nitric oxide, could play a great part in the pathogenesis of HE as it leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, brain edema, and deterioration in cognitive functions. High arterial ammonia leads to impairment in mitochondrial functions with subsequent edema and swelling of the astrocytes. It has been documented in about 90% of patients with HE. Elevated arterial blood ammonia level is also considered an important underlying mechanism. One of the suggested theories is that increased gamma amino butyric acid in the central nervous system leads to an increase in the neuronal inhibitory effect.
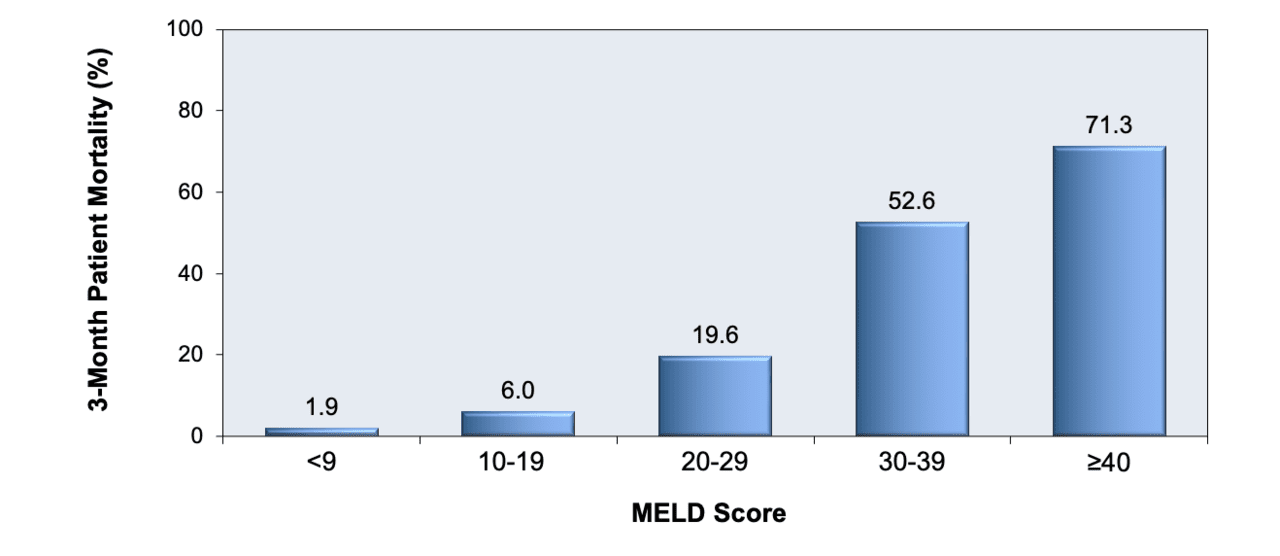
Īlthough the clear pathogenesis of HE is not evident, some mechanisms caused by liver insufficiency are proposed. A wide range of motor dysfunctions has been described in HE, including asterixis, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, and/or extrapyramidal manifestations. HE is clinically manifested as disorientation, confusion, inappropriate behavior, agitation, somnolence, stupor, and/or frank coma. The diagnosis of HE remains essentially clinical. It is one of the most serious complications of liver cirrhosis that leads to a significantly impaired quality of life and frequent hospitalizations. Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a brain dysfunction caused by impaired liver functions and/or portosystemic shunting. ConclusionsĬLIF-SOFA score was superior to other prognostic scores in predicting mortality in hospitalized patients with HE type C. Among these scores, CLIF-SOFA was the strongest independent predictor of mortality (OR = 1.142, CI95% = 0.888–1.467, p = 0.001). MELD, MELD-Na, and CLIF-SOFA scores were the independent predictors of mortality. All scores were significantly higher in the deceased patients. The main precipitating factors of HE was infections predominantly spontaneous bacterial peritonitis ( n = 108, 54.0%) followed by variceal bleeding ( n = 39, 19.5%). Backward logistic regression analysis was used to identify the predictors of mortality. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted, and the area under the ROC curve (AUROC) was calculated for each score. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data as well as prognostic scores were compared in both deceased and improved groups. According to survival outcomes, patients were categorized into either improved or deceased. APACHE II, CLIF-SOFA, MELD, MELD-Na, and CTP scores were calculated for all patients within the first 24 h after admission. Diagnosis and classification of HE were based on the West Haven criteria. Two hundred cirrhotic patients hospitalized with HE were included in the study. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of these scores in patients with HE on a background of liver cirrhosis (type C). These scores were thoroughly investigated in HE associated with acute liver failure (type A). The most used scores are Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP), Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD), Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (CLIF-SOFA), and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II). Many scoring systems are used to predict the outcome of HE in patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a serious condition associated with high rates of mortality.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
